1 Site setout
Where do we get our mark for the building line?
we get our building line when we set out our profiles, and then we set out the building line at what ever on the plain and sepecification, the building line is inside the profiles.
What is a building line?
a building line is a line we can start to build in
What is a Profile how is it constructed ,What materials used ,what size?
a profile is piesces of wood that helps us guide where to construct, the material used in it is planks of wood and wooden posts
How do we square the building lines?
we can square a building going diagonal one end of the building line to the other, we do this on both sides and if it is square the numbers will be the same
Name all the parts?
2 Power tool safety
Skill Saw,Beltsander, jig saw, drill,Thickness-er, buzzer, nail gun gas powered, air?
Discribe what each tool does?
Skill Saw
is a machine where you can cut a straight line, diagonal or reduce the thickness
Beltsander
is a machine that saves you time in sanding by hand this will only take a few minuters to sand a piece of wood.
Jig Saw
is a machine that you can cut inside a piece of wood this is better then using a skill saw cause you can do alot that a skill saw cant do.
Drill
this machine drills holes in a piece of wood
Thickness-er
this machine saves time in planning it will reduce the thickness of the piece of wood while having a clean finish
Sunday, March 27, 2011
Thursday, March 17, 2011
Sub floor flooring Research
Tempory sub flooring
temporay sub flooring is a sturdy piece of wood which you can use anywhere in a house it is excellent for heavy load where it can support the weight of vehicles and other heavy objects, it is easy to be assembled into any shape and easily alligned and releasably locked togeather. the good things about sub flooring is sub flooring is its cost effective, easy for storage and some sections of it kan be reused.
A method of assembling a temporary flooring assembly is also disclosed. A plurality of rectangular sections are provided. each of the sections has first and second ends and first and second sides, with a keying means extending from the first end and a locking means formed in the second end. a pair of slots are formed in the respective first and second sides of each section. a cam lock is rotatably secured proximate the first side adjacent the first side slot. the cam lock has an arm pivotally moveable through the first side slot. the first side of one of the sections is aligned with the second side of another of the sections so that the slots are aligned. the cam lock is pivoted so that the arm passes through the first side slot and into the second side slot, thereby securing the first and second sides togetha
Bearers
Single span joists are set between and are supported off a T section bearer. This produces a shallower floor than conventional bearer and joist arrangements.
 Sub floor frame: Joists on bearer
Sub floor frame: Joists on bearer The conventional arrangement in sub floor frames is for joists to run over the top of bearers. Joists and bearers are regularly used as continuous span elements running the full length or width of the building.
Sub floor frame: Inline joists fixed to bearer with joist hangers.
Single span joist are set between the bearers and supported with proprietary sheet metal beam hangers. This produces a shallower floor than conventional bearer and joist arrangements.
floor joists
floor joists is the important pat of the building, floor joists are the one that hold the weight of the building, asorb impacts on the floor and it will make the building floor stable and secure
Insulation
insulation preety much is for the confort of the occupant that is in living in the house, insulation creates warmth and keeps in the warmth if using the heater or fireplace, and it can also reduce noise ion between the house.
Stud
A vertical framing member used to construct walls.
under stud
Framing stud that is cut to fit between the bottom plate and the header, beam or lintel.
lintel
A beam placed perpendicular to wall studs above doors, windows or other openings to carry the weight of structural loads.
bottom plate
Wall plate, sole plate; The bottom horizontal framing member of the wall. The bottom, horizontal structural member of a stud framed wall. The bottom plate sets on the subfloor or attached to the foundation and nailed to the bottom of the wall studs.
top plate
the top horizontal framing member of the wall. A horizontal framing member laid at and nailed to the top of the vertical studs. Top horizontal member of a frame wall supporting ceiling joists, rafters, or other members.
the top horizontal framing member of the wall. A horizontal framing member laid at and nailed to the top of the vertical studs. Top horizontal member of a frame wall supporting ceiling joists, rafters, or other members.
Monday, March 14, 2011
14/03/11
for first block we were in the computer lab we we doing:
- assignment 2 which was to find out what types of timber used in the constuction industry (New zealand)and how we treat timber.
- we also did a research on work horse/ saw horse
Sunday, March 13, 2011
Assignment 2
what type of timber is used in the construction industry and what is involved in treating the wood?.
- Rimu
- Radiota Pine
- Fijian kauri
- Oak
- Kwila
- Balau
- macrocarpa
- Eucalypt Species
For timber framed buildings most of the timber used must be treated to prevent damages within the wood by insects and moisture. the treatment is accordance with nzs 3640 which will normally be:
- Baron salts (H1.1, H1.2)
- Light organic solvent persavative (H.1, H1.2, H3.1, H3.2)
- Copper chrome asenate (H3.2, H4, H5, H6)
- Amoniacal or alkaline copper quaternary (H3.1, H3.2, H4, H5)
- Copper Azole (H3.1, H3.2, H4)
When using copper - based treated timber for exposed situation:
- site treat cut ends
- do not place cut ends in the ground
- do not burn off - cuts on barbecues or in domestic fireplaces
H1.1 - framing to external wall clad with masonary
H1.2 - enclosed subfloor framing
H3.1 - exterior plywood- painted
H3.2 - exposed subfloor - unpainted
H4 - exposed subfloor framing
H5 - veranda posts in the ground.
Tuesday, March 8, 2011
07/02/2011
Day 6
Today we were continuaing with our joint and drawing boards in the workshop , after lunch break we were in the class room discussing the tools we used, the safety aspects for the machine, and i also learnt what 5x5 is.
These are the machines we were discussing and what safty aspects are:
Router
The router is a power tool used to rout out an area in the face of a piece of wood and the outside of the wood.
the safety aspects for it is:
- hold both sides of the router for full control
- dont put your hands where the bit is
- and check the tags on it
Jigsaw
safety aspects for this machine:
- dont put your hand down the bottom of the jigsaw
- wait for the blade to stop before moving the machine
- if holding the machine with one hand dont hold it carelessly
- and always check the tags.
Monday, March 7, 2011
111era assignment 1
What is the building act and schedule??
What is the building regulation??
Building act
the building act is a ledgislation which helps aid the building industry, this act helps encouragin better practices, building design and constructionwhich means:
- more understanding on what the standards are and what they expect buildings to meet.
- more tougher in the building consent and inspection process.
- more certain that capable people are doing the building design, construction and inspection
- better protection for homeowners through the introduction of mandatory warranties.
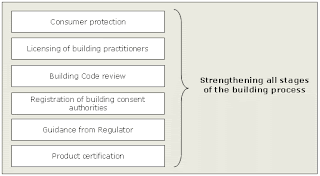
The building act has 5 parts which provides the framework for new zealand building control system:
part 1: The purpose and principles of the Building Act, together with an overview, and commencement dates for various provisions and definitions. These sections provide an important reference point for reading and interpreting the Building Act.
part 2: Matters relating to the Building Code and building work
part 3: Sets out the functions, duties and powers of the chief executive of the Department of Building and Housing, territorial authorities, regional authorities, and building consent authorities. It also deals with the accreditation of building consent authorities and dam owners, and product certification.
part 4: Matters relating to the licensing and disciplining of building practitioners
part 5: Miscellaneous matters including offences and criminal proceedings, implied terms of contracts, regulation-making powers, amendments to other enactments and the repeal of the Building Act 1991, and the transitional provisions from the Building Act 1991 to the Building Act 2004
Building Regulation
building regulation form an important part of new zealnd building control, they are made up in accordance with he the building act 2004. the building regulation 1992 were made under the building act 1991 however most of the 1992 regulation was revoked on 31 march 2005 by the building regulation 2004, the types of regultion the can be made (including the process) must be followed when creating new regulation are givin in sections 400-415 of the act.
- 1992/150: Building Regulations 1992
- 2004/385: Building (Forms) Regulations 2004
- 2005/032: Building (Specified Systems, Change the Use, and Earthquake-prone Buildings Regulations 2005
- 2005/033: Building Levy Order 2005
- 2005/055: Building (Fee for Determinations) Regulations 2005
- 2007/403: Building (Infringement Offences, Fees, and Forms) Regulations 2007
- 2008/208: Building (Dam Safety) regulations 2008
- 2008/360: Building (Product Certification) Regulations 2008
- 2009/408: Building (Minor Variations) Regulations 2009
- 2009/409: Building (National Multiple-use Approval) Regulations 2009
Building Consent Authorities
- 2006/399: Building (Accreditation of Building Consent Authorities) Regulations 2006
- 2007/102: Building (Consent Authority Accreditation Fees) Regulations 2007
- 2007/300: Building (Registration of Building Consent Authorities) Regulations 2007
Licensed Building Practitioner Regulations
- 2007/125: Building (Design Work Declared to be Building Work) Order 2007
- 2008/304: Building Practitioners (Complaints and Disciplinary Procedures) Regulations 2008
- 2010/043: Building (Designation of Building Work Licence Classes) Order 2010
- 2010/044: Building Practitioners (Licensing Fees and Levy) Regulations 2010
- 2010/045: Building Practitioners (Register of Licensed Building Practitioners) Regulations 2010
Building schedual 1
shedueal 1 enables building owners to repair and maintain their buildings without having to get a building consent, provided they use comparable materials, components or assemblies in the same position. Additional guidance is available about this exemption in the Department's past Codewords publications. There have also been a number of determinations that discuss the use of comparable
building consent is not required for the following building work:
- any lawful repair and maintenance using comparable materials, or replacement with a comparable component or assembly in the same position, of any component or assembly incorporated or associated with a building, including all lawful repair and maintenance of that nature that is carried out in accordance with the Plumbers, Gasfitters, and Drainlayers Act 2006,
- repair or replacement (other than maintenance) of any component or assembly that has failed to satisfy the provisions of the building code for durability, for example, through a failure to comply with the external moisture requirements of the building code; or
- repair or replacement of a water storage heater connected to a solid-fuel heater or other supplementary heat exchanger
Sunday, March 6, 2011
02/03/2011
Day 5
Today i went to the library which is in south campus we were shown around the libary, what i learnt is where the library is, whats in the library and where the stuff is in the libary e.g books, computer and etc
aftter mornning break we were in the computer room doing a numeracy test. we did the numracy test so our tutor knows what level we are on and what he can do to help me out.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)